Publications
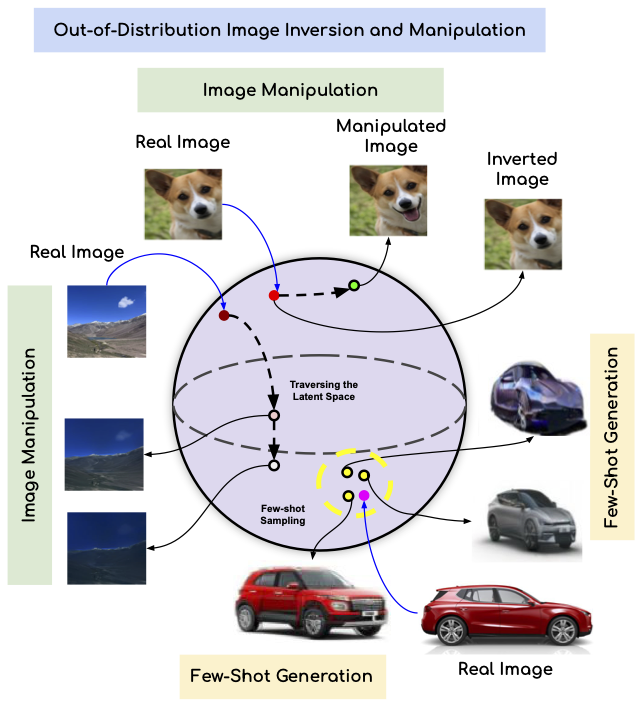
This work tackles the important task of understanding out-of-distribution behavior in two prominent types of generative models, i.e., GANs and Diffusion models. Understanding this behavior is crucial in understanding their broader utility and risks as these systems are increasingly deployed in our daily lives. Our first contribution is demonstrating that diffusion spaces outperform GANs’ latent spaces in inverting high-quality OOD images. We also provide a theoretical analysis attributing this to the lack of prior holes in diffusion spaces. Our second significant contribution is to provide a theoretical hypothesis that diffusion spaces can be projected onto a bounded hypersphere, enabling image manipulation through geodesic traversal between inverted images. Our analysis shows that different geodesics share common attributes for the same manipulation, which we leverage to perform various image manipulations. We conduct thorough empirical evaluations to support and validate our claims. Finally, our third and final contribution introduces a novel approach to the few-shot sampling for out-of-distribution data by inverting a few images to sample from the cluster formed by the inverted latents. The proposed technique achieves state-of-the-art results for the few-shot generation task in terms of image quality. Our research underscores the promise of diffusion spaces in out-of-distribution imaging and offers avenues for further exploration.
Sai Niranjan Ramachandran, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Madhav Agarwal*, C.V. Jawahar, Vinay Namboodiri
*These authors contributed equally.
38th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI), 2024 (Oral)
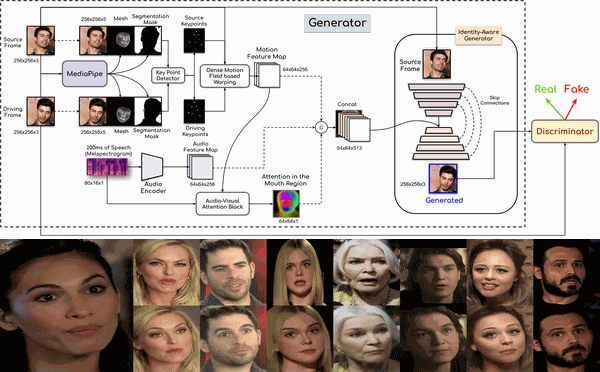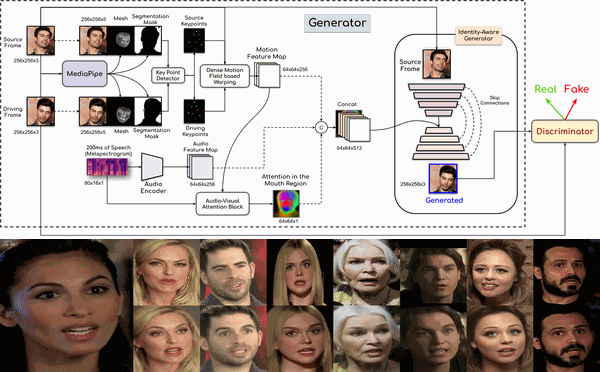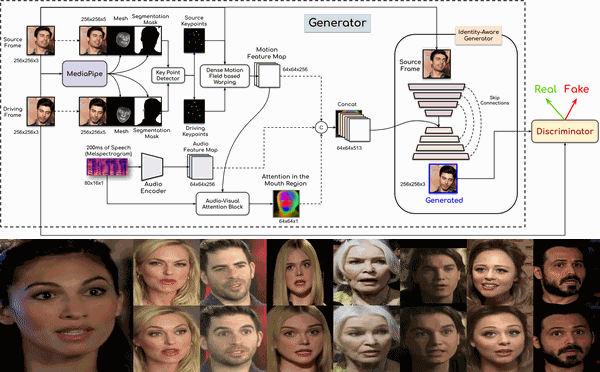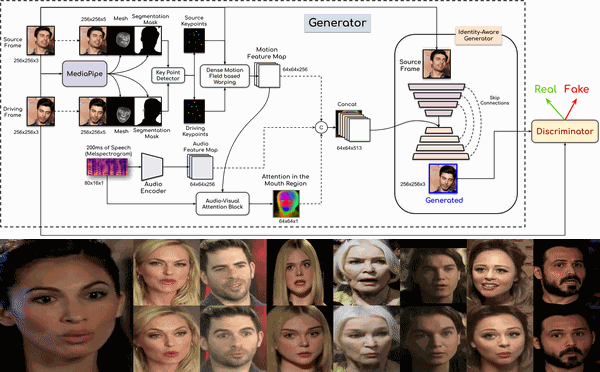
This work proposes a novel method to generate realistic talking head videos using audio and visual streams. We animate a source image by transferring head motion from a driving video using a dense motion field generated using learnable keypoints. We improve the quality of lip sync using audio as an additional input, helping the network to attend to the mouth region. We use additional priors using face segmentation and face mesh to improve the structure of the reconstructed faces. Finally, we improve the visual quality of the generations by incorporating a carefully designed identity-aware generator module. The identity-aware generator takes the source image and the warped motion features as input to generate a high-quality output with fine-grained details. Our method produces state-of-the-art results and generalizes well to unseen faces, languages, and voices. We comprehensively evaluate our approach using multiple metrics and outperforming the current techniques both qualitative and quantitatively. Our work opens up several applications, including enabling low bandwidth video calls.
Madhav Agarwal, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar
Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV), 2023
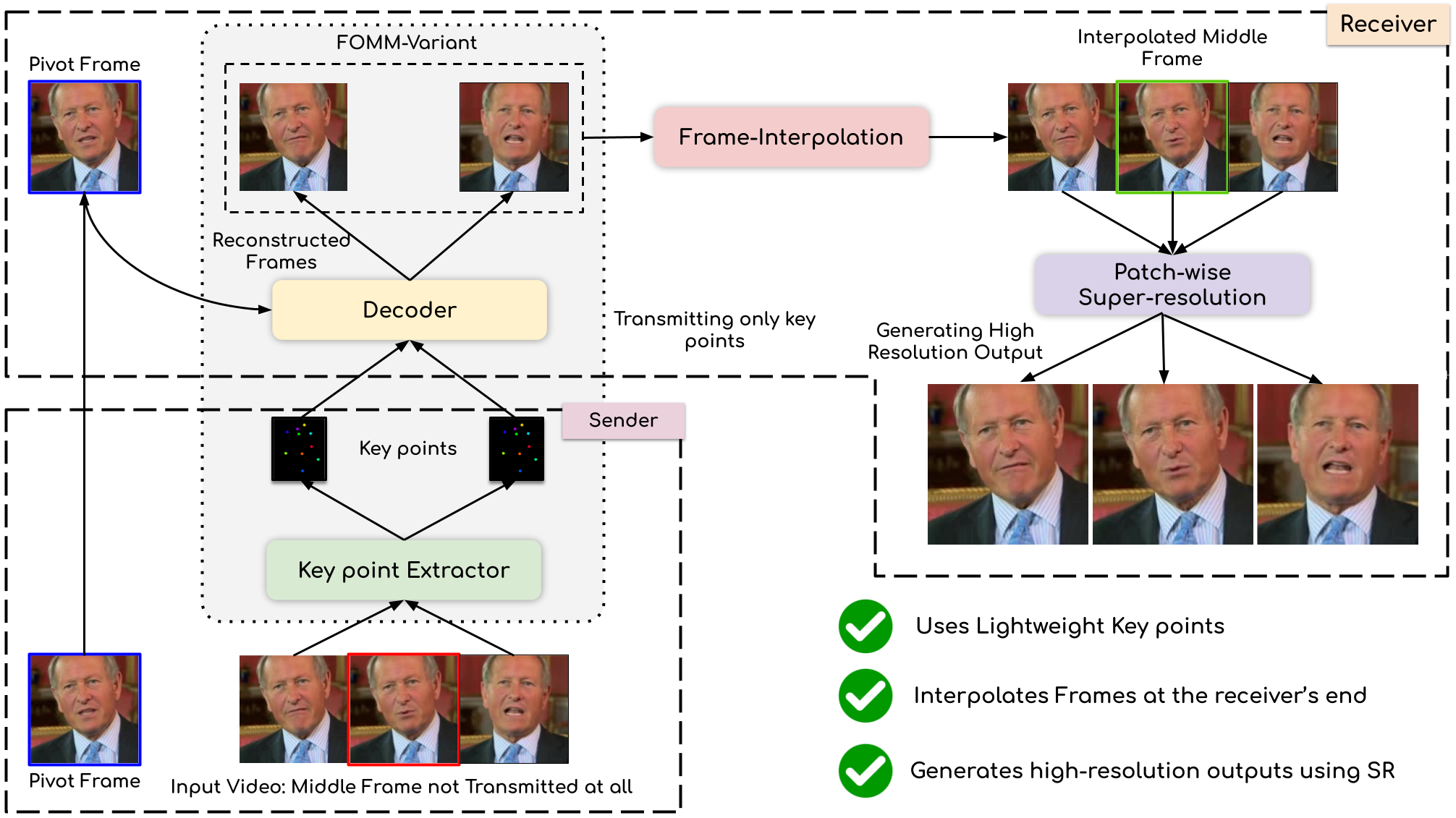
We leverage the modern advancements in talking head generation to propose an end-to-end system for talking head video compression. Our algorithm transmits pivot frames intermittently while the rest of the talking head video is generated by animating them. We use a state-of-the-art face reenactment network to detect key points in the non-pivot frames and transmit them to the receiver. A dense flow is then calculated to warp a pivot frame to reconstruct the non-pivot ones. Transmitting key points instead of full frames leads to significant compression. We propose a novel algorithm to adaptively select the best-suited pivot frames at regular intervals to provide a smooth experience. We also propose a frame-interpolater at the receiver’s end to improve the compression levels further. Finally, a face enhancement network improves reconstruction quality, significantly improving several aspects like the sharpness of the generations. We evaluate our method both qualitatively and quantitatively on benchmark datasets and compare it with multiple compression techniques.
Madhav Agarwal, Anchit Gupta, Rudrabha Mukhopadhyay, Vinay Namboodiri, C.V. Jawahar
33rd British Machine Vision Conference (BMVC), 2022
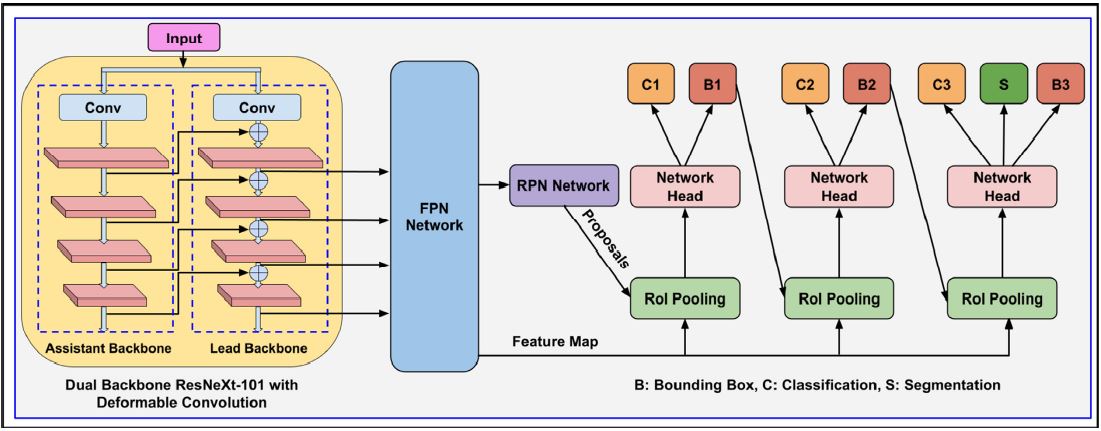
Localizing document objects such as tables, figures, and equations is a primary step for extracting information from document images. We propose a novel end-to-end trainable deep network, termed Document Object Localization Network (dolnet), for detecting various objects present in the document images. The proposed network is a multi-stage extension of Mask r-cnn with a dual backbone having deformable convolution for detecting document objects with high detection accuracy at a higher IoU threshold. We also empirically evaluate the proposed dolnet on the publicly available benchmark datasets. The proposed DOLNet achieves state-of-the-art performance for most of the bench-mark datasets under various existing experimental environments. Our solution has three important properties: (i) a single trained model dolnet that performs well across all the popular benchmark datasets, (ii) reports excellent performances across multiple, including with higher IoU thresholds, and (iii) consistently demonstrate the superior quantitative performance by following the same protocol of the recent works for each of the benchmarks.
Ajoy Mondal, Madhav Agarwal, C.V. Jawahar
Pattern Recognition, Volume 142, 2023
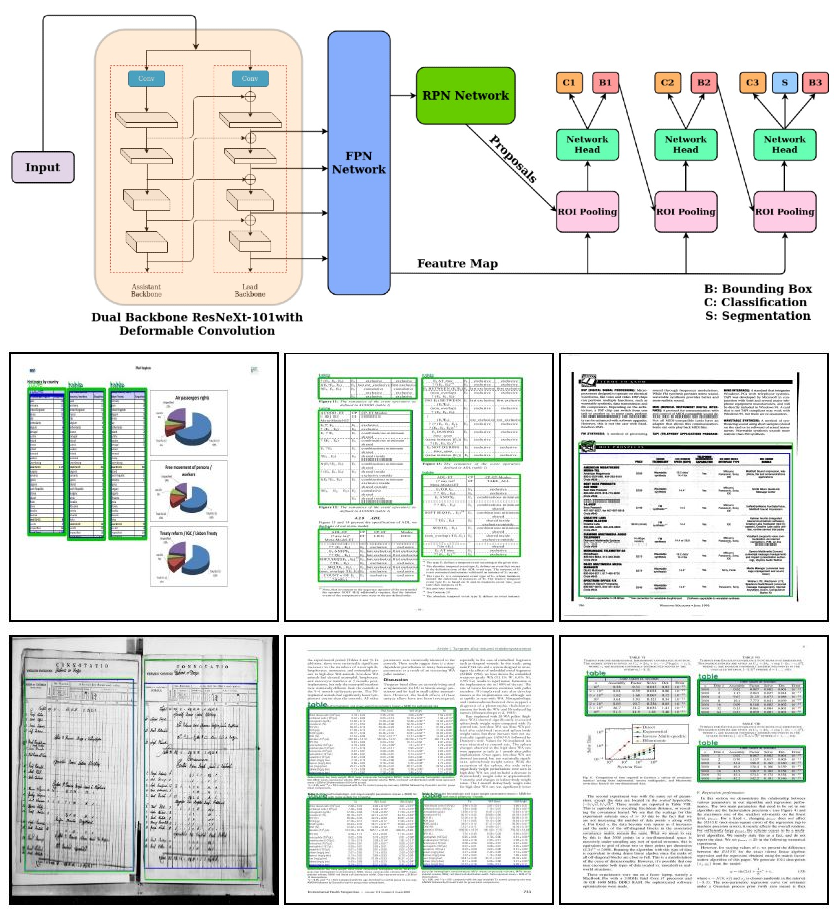
Localizing page elements/objects such as tables, figures, equations, etc. is the primary step in extracting information from document images. We propose a novel end-to-end trainable deep network, (CDeC-Net) for detecting tables present in the documents. The proposed network consists of a multistage extension of Mask R-CNN with a dual backbone having deformable convolution for detecting tables varying in scale with high detection accuracy at higher IoU threshold. We empirically evaluate CDeC-Net on the publicly available benchmark datasets with extensive experiments. Our solution has three important properties: (i) a single trained model CDeC-Net‡ that performs well across all the popular benchmark datasets; (ii) we report excellent performances across multiple, including higher, thresholds of IoU; (iii) by following the same protocol of the recent papers for each of the benchmarks, we consistently demonstrate the superior quantitative performance. Our code and models are publicly available for enabling reproducibility of the results.
Madhav Agarwal, Ajoy Mondal, C.V. Jawahar
25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition (ICPR), 2020 (Oral)